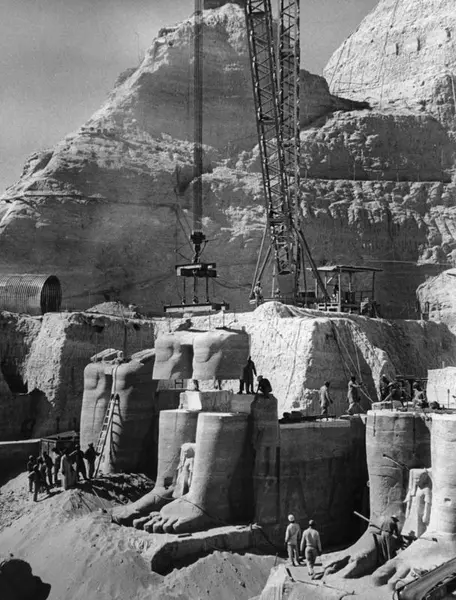
Demonteringen av statuene i Abu Simbel-tempelet. UNESCO
UNESCO
UNESCO is the United Nations' organization for education, science, culture and communication. In 1972 UNESCO ratified a convention for the preservation of world culture and natural heritage – the World Heritage Convention.
UNESCO was established after The Second World War (1939–1945). Representatives from 45 countries met in London to create an organization that would embody a genuine culture of peace. In their eyes, the new organization had to establish the “intellectual and moral solidarity of mankind” and, in so doing, prevent the outbreak of another world war. UNESCO's mandate is to contribute to peace and security by promoting cooperation between nations within education, science, culture and communication.
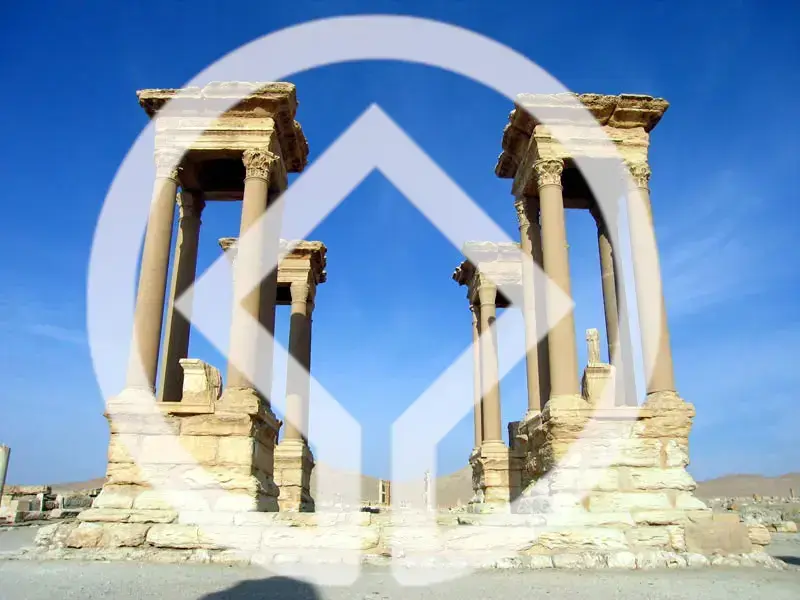
In the late 1950's the southernmost relics of the ancient human civilization of Nubia in Egypt were under threat from the rising waters of the Nile that were about to result from the construction of the Aswan High Dam. In 1959, an international donations campaign to save the monuments began. The campaign was supported by more than 50 countries. During the 20-year campaign, 22 monuments and architectural complexes were relocated.
The Nubia campaign showed how important solidarity and cooperation between nation states is in order to protect unique monuments. The result was the launching of more campaigns, including Moenjodaro in Pakistan, Fez in Morocco, Kathmandu in Nepal, Borobudur in Indonesia and the Acropolis in Greece. Another result of the Nubia campaign was that UNESCO started to plan the World Heritage Convention.
UNESCO's World Heritage Convention
In 1972 UNESCO ratified the convention for the preservation of world culture and natural heritage.
The Convention established a system for making a list of places in the world, which, because of their universal value, should be considered as world heritage sites for future generations, and the whole of humanity.
In accordance with the Convention, an international committee dealing with world heritage issues was formed. The committee held its first meeting in Paris in 1977. At the committee’s second meeting the first 12 sites, among them the Galapagos Islands, the historical centre of Krakov and Yellowstone Park, were approved and inscribed on UNESCOs World Heritage List.
In 2018, 1073 places are listed on the World Heritage list. Here is an updated version of the list: http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/